In focus: NVIDIA Quadro P1000
The NVIDIA Quadro P1000 is one of the most popular models for multi-monitor solutions in compact systems. Despite the availability of newer models such as the RTX A2000, the P1000 impresses with:
- Compact design and low power consumption
- 4 simultaneous display outputs via Mini-DisplayPort
- Full support for NVIDIA Mosaic
- Stable performance in 2D and 3D applications
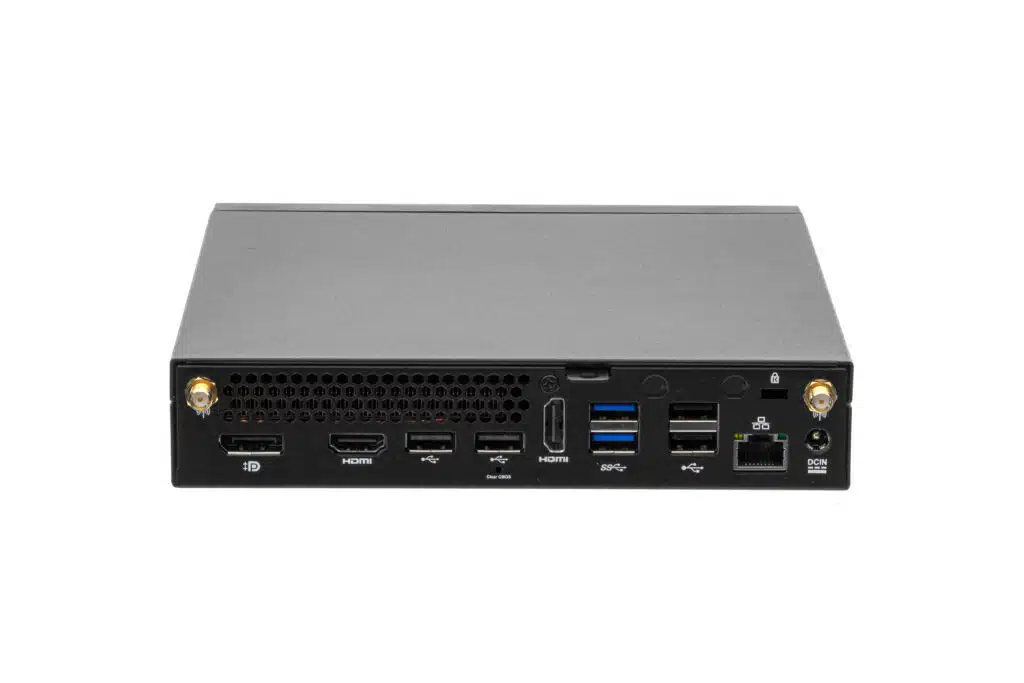
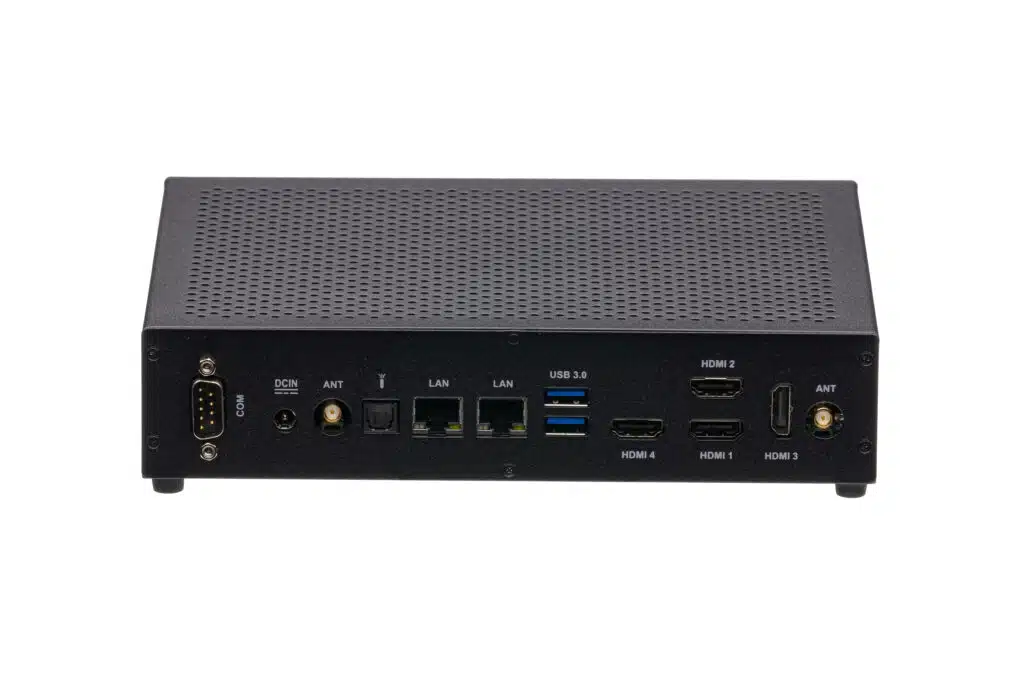
In the series of spo-comm Mini-PCs, the QUADRO P1000 is equipped with the eponymous P1000 and therefore 640 CUDA cores as standard, and up to four monitors can be controlled simultaneously.


NVIDIA Mosaic and desktop management
A decisive advantage of the Quadro series is NVIDIA Mosaic: With this technology, the Windows desktop can be stretched across several screens without display errors or synchronization problems.
Specific features such as MOSAIC are set via the graphics card driver and the associated management tool. At Nvidia, this is called the Nvidia Control Panel. Nvidia shows how MOSAIC can be configured with a graphics card from this series on this knowledgebase.
In addition, professional tools such as the NVIDIA RTX Desktop Manager (successor to Nview) are available for clear multi-display management.
Multi-GPU setups – not a good idea?
Although it is technically possible to operate both series in parallel, driver conflicts often occur in practice. In most cases, only one driver type can be operated stably. For professional multi-monitor setups, it is therefore advisable to opt for a purely Quadro-based solution.
Future-proof with NVIDIA RTX A-Series
For particularly demanding applications, models such as the NVIDIA RTX A2000, A4000 or A4500 are now available on the market. These cards also support NVIDIA Mosaic, offer even more computing power and are suitable for setups with up to 32 screens (in conjunction with NVIDIA RTX Sync solutions).
Nevertheless, the P1000 remains a cost-effective and robust solution for many scenarios, especially when it comes to compact, fanless systems or durable industrial PCs.
GeForce vs. Quadro – the most important differences
NVIDIA GeForce graphics cards are primarily designed for gaming and general graphics performance. They deliver solid results in the multi-monitor area, but there are some limitations for professional environments – especially in terms of driver stability, long-term availability and management functions.
NVIDIA Quadro cards, such as the P1000, have been specially developed for professional use. They offer, among other things:
- Certified drivers (ISV certification) for software such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Adobe and more
- NVIDIA Mosaic technology for seamless display of a desktop across multiple monitors
- Long-term availability – important for industrial customers
- High image quality and color fidelity
- Multiple native Mini-DisplayPort outputs(e.g. 4x mDP on the P1000)
Our conclusion – there is no way around Quadro for professional multi-monitoring
Whether 2, 3 or 4 monitors – if you need a reliable and flexibly expandable multi-screen setup, a P1000 graphics card – and the spo-comm QUADRO P1000 – is the perfect choice.
The range is perfectly complemented by the RUGGED T1000, which is also equipped with a high-performance Quadro graphics card and thus delivers maximum graphics power in a compact format.
The graphics card combines professional functions with high compatibility in space-saving devices.
Incidentally, in addition to the Quadro graphics card, our portfolio also includes industrial PCs with an NVIDIA RTX graphics card. For example, our NOVA R680E, the NINETEEN Q670E or the KUMO VI!