09.09.2019

Both serial and parallel interfaces are used for the physical exchange of data between computers and peripheral devices. The term "serial" comes from the fact that the data bits are transmitted one after the other on a line during this process.
With parallel interfaces, the bits are not transmitted one after the other but - as the name suggests - in parallel. Nowadays, the term parallel interface usually refers to the IEEE 1284 connection, which is often also called the printer interface.
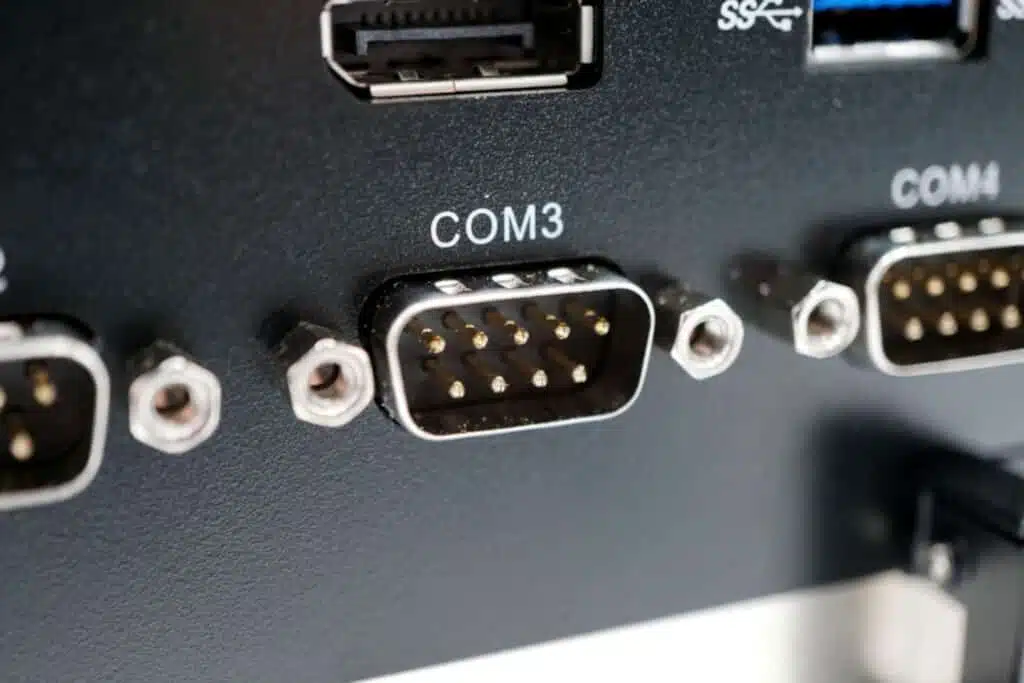
If we now look at the serial interfaces of a (mini) PC, the term usually refers to an RS-232 interface. However, this is better known by its English name COM port. RS-232 was developed back in 1960 for the telecommunications and IT sectors. Thanks to its simple implementation and reliability, the interface was also used in the field of consumer electronics. The RS-232 specifications were last updated in 1997. On PCs and laptops, the RS-232 was used for a long time to connect keyboards or mice, but has since been replaced by the faster and smaller USB port.
As is usual for serial interfaces, RS-232 also transmits the bits one after the other via the connection line. With RS-232, data is transmitted word by word and asynchronously. You can find out exactly how this works here.
Originally, the RS-232 interface is a 25-pin Sub-D connector. However, as not all signals provided by this standard are required in IT, the 9-pin Sub-D connector has become established (see Fig. 1). If several of these ports are installed on a PC, the physical interfaces are assigned a logical designation, COM 1, COM 2, and so on, by the BIOS and the operating system (see Fig. 1).
As with other cables, such as HDMI, the speed of data transmission depends on the cable length, among other things. No maximum cable length has been defined for the RS-232 standard, only its maximum capacity. This 2500 pF is achieved with a cable length of approx. 15 meters. If cables with an extremely low capacitance are used, even up to 45 meters can be achieved.
Table of cable lengths and data rates
Even today, in the age of Industry 4.0, many technical devices in the industrial sector cannot do without a serial interface. The RS-232 is convincing in this area with its functionality, which can be implemented easily and inexpensively, and also because the interface is supported by most manufacturers and users.
In contrast to the Universal Serial Bus (USB), RS-232 as a communication interface does not require a special driver for the operating system used. This results in lower support costs and protection against system crashes in the event of possible programming errors in the driver. Problems with the COM port are rare in practice. If problems do occur, it is possible to simply replace the hardware without having to intervene in the sensitive software environment.
Safety plays a key role in the industrial sector anyway. The COM port can also score points here: The cable gland protects the inside of the PC from dust or moisture in production halls, which in turn can improve the health of a Mini PC and increase its service life.
In addition to the COM port, there are also other serial interfaces that have a place in some of our Mini PCs. On the one hand there is the RS-422 standard, also known as EIA-422, and on the other hand the RS-485 or EIA-485 standard.
The RS-422 stands for wired differential and serial data transmission. In contrast to RS-232 with unbalanced signal transmission, RS-422 requires balanced transmission.
The RS-485 or EIA-485 standard stands for asynchronous serial data transmission like RS-232, but also for symmetrical data transmission like RS-422.
As mentioned above, the maximum distance for RS-232 is 15 meters. In addition, this serial interface can only have one transmitter and one receiver, whereas the RS-422 can address up to 10 receivers and have a maximum line length of up to 1200 meters. The RS-485 goes one better with up to 32 receivers and up to 4000 meters of cable.

Edge AI is the combination of artificial intelligence and local data processing directly at the poin...

This was our start to the new year: the current memory and CPU situation continues to have a major i...
There is currently a global crisis in the areas of RAM bars and CPUs. What began last summer as a mo...
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information