09.01.2025

Both machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) are based on algorithms that learn from data. The difference lies in the complexity and structure of the models:
A simple example: While a classic ML model defines image features such as edges or shapes by hand, a DL model can extract these features independently from the raw data.
The system is based on neural networks inspired by the structure of the human brain. These networks consist of "neurons" that are arranged in several layers:
Each connection between the neurons has a weight that is adjusted during training to improve accuracy.
Mini PCs can also run complex deep learning applications thanks to powerful hardware and optimized software. We have put together a few examples:
Deep learning on mini PCs offers numerous advantages, but also presents some challenges. The compact design of the mini PCs is an advantage, and the little helpers are also more energy and cost efficient than traditional servers.
However, there are challenges in terms of limited computing power and memory. However, special hardware such as AI accelerators (e.g. NIVIDIA Jetson Nano) can partially overcome these limitations.
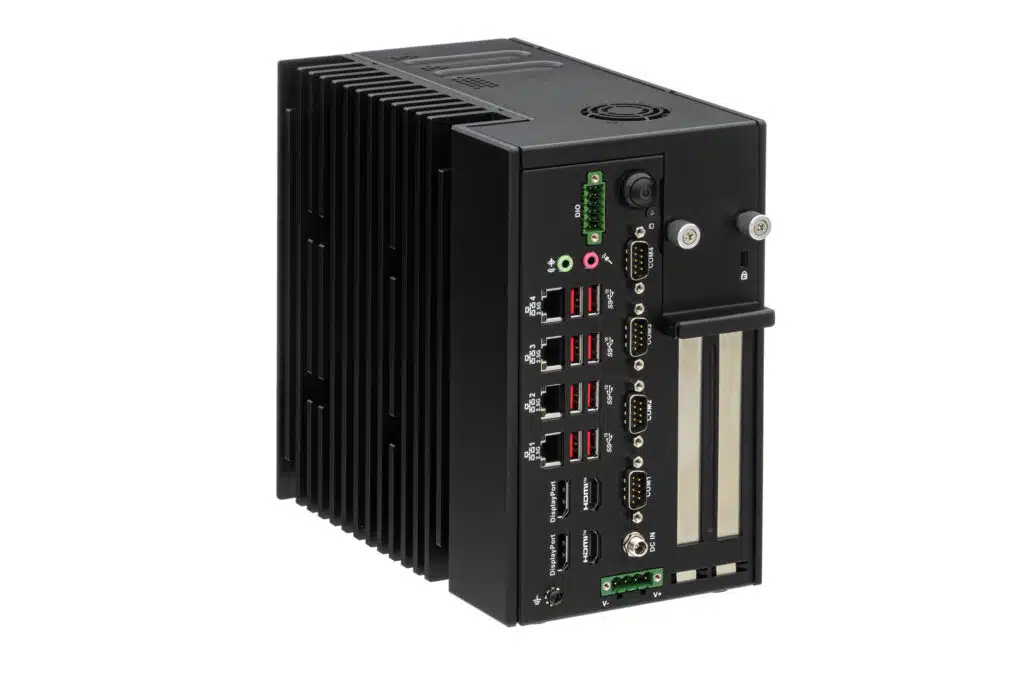



Our product portfolio also includes the odd mini PC that masters deep learning with flying colors. Like our NINETEEN Q670E, for example, which should not be reduced solely to its 19-inch size, but also to what's inside it. The NINETEEN impresses with an Intel® Core™ i5-12500T CPU, up to 65GB RAM and optional NVIDIA RTX graphics card. It also offers some special features, such as a PCIe slot for an additional graphics card, RAID array with multiple SSDs, iAMT, Wake on LAN and much more!
In addition to the NINETEEN, our new CORE 5 Ultra also impresses with its high computing power for data-intensive applications. With its namesake Intel® Core™ Ultra 5 processor, compact format and numerous features, it is suitable for numerous applications. Whether 24/7 operation, demanding visualization or control tasks or embedded applications, the CORE 5 Ultra gets the best out of itself with maximum connectivity and NPU !
Our NOVA R680E should also not be forgotten for deep learning. In addition to extremely high connectivity and PCIe slots, it has fanless cooling, which also makes it attractive for harsh environments. The NOVA is also shock-tested in accordance with IEC 60068-2 and has an anti-vibration design. Speaking of connectivity - to remain versatile, it is equipped with 4 video outputs (2x HDMI 2.0 and 2x DisplayPort 1.4a), four COM interfaces, four 2.5Gbps LAN ports and 10 USB 3.2 ports on the front and back panel.
Deep learning is revolutionizing numerous industries and is becoming increasingly accessible, even on mini PCs. From image and speech recognition to industrial applications - the possibilities are almost limitless.
Whether in research, industry or the smart home sector - mini PCs make deep learning more tangible and affordable. With the right combination of hardware and software, (almost) no AI application stands in the way!

Edge AI is the combination of artificial intelligence and local data processing directly at the poin...

This was our start to the new year: the current memory and CPU situation continues to have a major i...
There is currently a global crisis in the areas of RAM bars and CPUs. What began last summer as a mo...
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information