02.05.2016
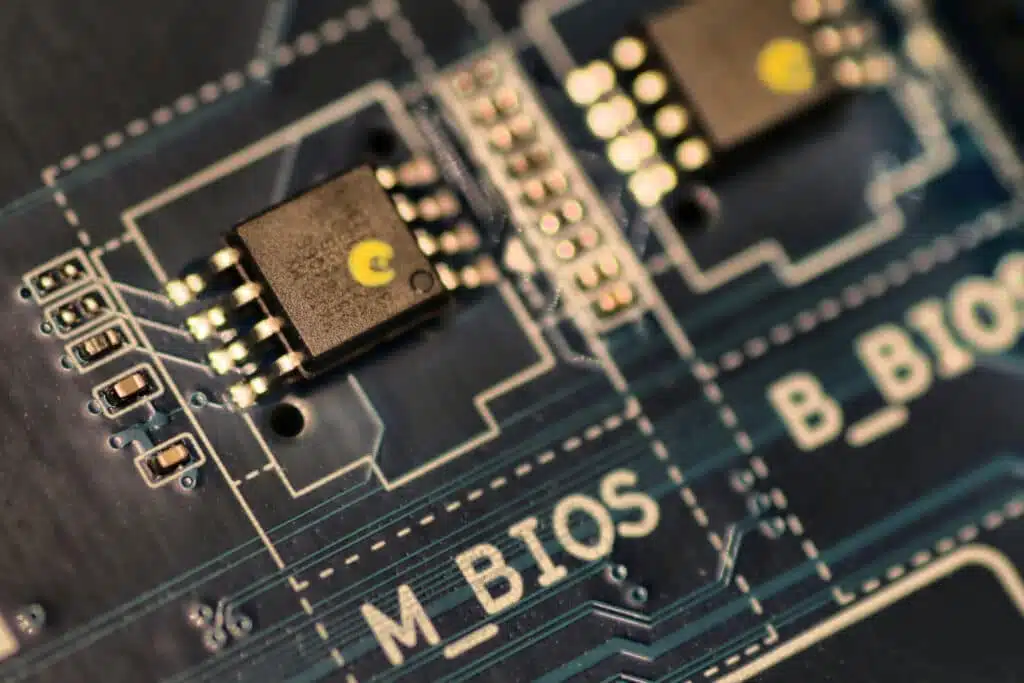
The abbreviation BIOS stands for "Basic Input/Output System". It is the firmware of a PC - software that is permanently built into the hardware. The BIOS is stored on a small chip in the computer's mainboard and is always pre-installed. Some mainboards have a second chip that acts as a backup. The BIOS forms the link between software (operating system) and hardware components such as hard disks, keyboard, mouse and printer. The BIOS can only be operated via the keyboard.
The successor to the BIOS is UEFI, which stands for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, i.e. a standardized extensible firmware interface. UEFI looks like an operating system, but - unlike BIOS - can be operated with the mouse and is able to run programs.
The main tasks of the BIOS are a self-test and the initialization of the hardware as well as the communication between the operating system and other components. When a computer is switched on, the BIOS starts up immediately and prepares the PC for booting. The power-on self-test (POST) is carried out first. The computer checks one after the other whether the basic hardware components, such as CPU and RAM, are working. If errors are detected, the BIOS indicates this with special tones or, if the graphics have already been successfully checked, on the screen.
After this self-test, it's time to boot. To do this, the hardware must know from which component the operating system is to be started. The BIOS therefore searches the available drives (hard disks, USB, DVD) in a specific order according to the operating system. As soon as it finds a software, the PC is started automatically. The order of the drives on which the operating system is searched for can be defined in the BIOS as required. For example, if you want to delete the existing operating system and install a new one via DVD, it is necessary to set the DVD drive to the first position. Other BIOS tasks include managing the date and time and monitoring the temperature of the processor and mainboard.
To access the BIOS, a specific key must be pressed immediately after switching on the PC and before starting the operating system (several times in succession!). Which button it is differs depending on the manufacturer. As a rule - and also with all spo-books - you can access the BIOS by pressing the "F2" or "Del" key.
Classic areas of application for industrial PCs and embedded systems are - as the name suggests - in...
Choosing the right hardware components is crucial to optimally equip Mini PCs for their area of appl...

In the modern world of mini PCs, reliability and security are an absolute must. One of the most impo...
I have read the data protection information.
Otto-Kraus-Straße 4c
D-90411 Nuremberg
Phone: +49 (0) 911 / 23 98 37 – 0
E-mail: info@spo-comm.de
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information