23.04.2019

The abbreviation UEFI stands for "Unified Extensible Firmware Interface". It is the successor to the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and is much easier to use. UEFI is an interface between the firmware, the individual hardware components of the computer and the operating system. UEFI has the same basic functions as the BIOS. It initializes the hardware, tests the individual hardware components and initiates the start of the operating system.
BIOS was developed back in the 1970s for the first IBM PC, which appeared in 1981. So it's not surprising that it's getting a bit long in the tooth. Because it is not 64-bit-capable, BIOS no longer met the requirements of newer hardware. Intel then took the first step and developed the successor EFI, which was specified in 1998. In order to further develop EFI, the Unified EFI Forum was founded, which includes Intel, AMD, Microsoft and other manufacturers. The first version of UEFI was finally released in 2006 and has been supported by Windows since Windows Vista.
Probably the most important new feature of the UEFI is Secure Boot, which increases the security of the boot process. It prevents malware from being loaded during the boot process, which could then manipulate or attack the computer. This is done using a digital key with which the boot loader and programs must identify themselves. If software is present that cannot authenticate itself, the system is prevented from starting.
If you want to access the UEFI, on most computers you have to press the "Del" key several times in quick succession immediately after switching on the PC. If this does not lead to success, it is worth taking a look at the manual. In some cases, it is a different key that enables access to the BIOS or UEFI.

For the last time this year, it's "What's New?" at spo-comm. We still have important information to ...
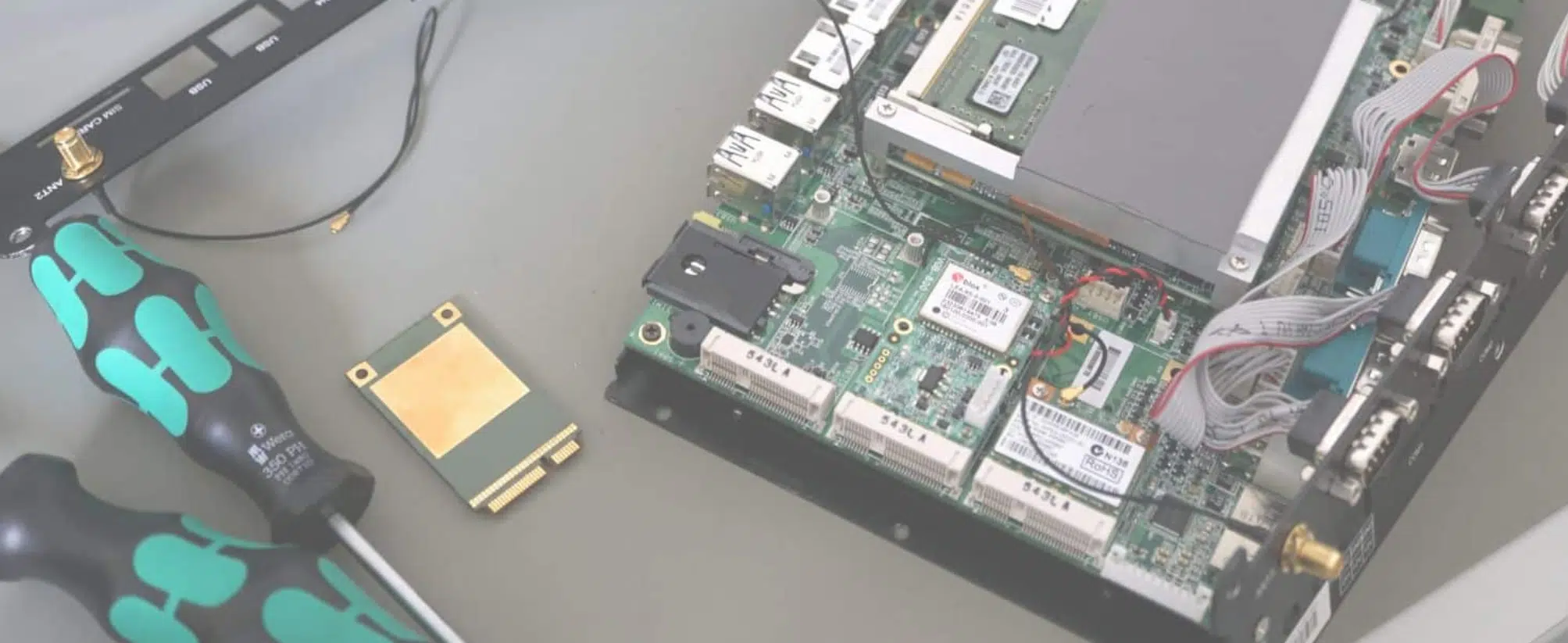
The form factor is particularly important in the development of Mini PCs for industrial and embedded...

In an era where technology is growing exponentially, machine learning is having a groundbreaking imp...
I have read the data protection information.
Otto-Kraus-Straße 4c
D-90411 Nuremberg
Phone: +49 (0) 911 / 23 98 37 – 0
E-mail: info@spo-comm.de
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information